Ammonia (NH₃) is a very common chemical that serves as a base material for almost all nitrogen compounds, such as urea and ammonium salts.
The main source of ammonia in our environment is agriculture with its livestock farming and fertilization. However, non-negligible quantities of ammonia are also produced in many other areas, like industrial processes and DeNOx applications in the energy and transportation sector.
Ammonia is a pungent smelling gas that not only bothers our nose, but is also toxic and harmful to the environment. When reacting with other air pollutants, it is also forming particulate matter. For more sustainability and protection of our environment, emissions of ammonia must be reduced and monitored.
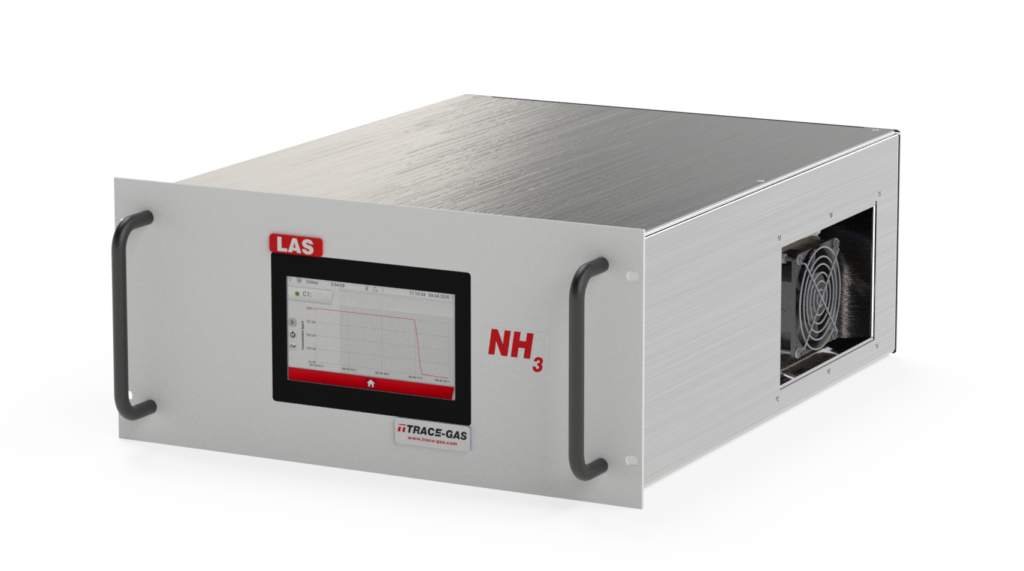
Our LASmini NH₃ analyzer, which is based on the selective method of laser absorption spectroscopy, is ideal for this purpose. It convinces by its fast response and easy handling. In the following we will present some interesting applications, in which ammonia plays a big role.

LAS mini NH3 in 19″ housing
Ammonia in the automotive industry
Due to the introduction of Adblue® technology in exhaust gas cleaning systems, ammonia (NH₃) plays a key role in the automotive industry nowadays. Ammonia (in the form of urea) is used to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in the exhaust gas by so called SCR systems. The injection of urea must be dosed precisely in order to achieve an efficient reduction of nitrogen oxides and avoid any residual ammonia to enter the environment. The remaining ammonia, also known as NH₃-slip, needs to be minimized and therefore monitoring solutions are required. Our LASmini NH₃ is used for direct measurements in hot and wet exhaust gases, which allows to monitor the real concentrations at each position of interest. Thus, exhaust gas cleaning systems can be monitored, evaluated or optimized regarding their NH₃ emission.
Ammonia in agriculture
Approximately 760,000 tons of ammonia are produced annually. 95% of this is produced in agriculture. NH₃ is released during decomposition of dead plants and animal excrements. Ammonia also escapes into the air through the storage and application of fertilizer (manure). Since many farmers operate biogas plants, ammonia emissions in agriculture have continued to rise. The environmental damage caused by acidic soils and fine particulate matter is toxic for sensitive ecosystems.
Potential of green ammonia
Technologies that use wind and solar energy to generate renewable energy have been around for some time now. With e-mobility and fuel cells, the automotive industry is to be driven away from fossil fuels. But where is the energy from wind turbines and photovoltaics stored so that the electricity is continuously available for driving? The same question arises when it comes to hydrogen for the fuel cell… This is where ammonia comes in: NH₃ can be used as energy storage for both renewable electricity and hydrogen. The prerequisite is the climate-neutral production of the so-called green ammonia. What does it take? Fresh air, water and renewable electricity. Let’s see where this green ammonia can be used advantageously:
✅ Decentralized energy storage for balancing power grids
✅ Hydrogen storage → NH₃ contains about 18% H₂
✅ Renewable fuel for modified power plants, engines and shipping
✅ Infrastructure already established by years of experience with ammonia as fertilizer
Do you need a suitable measuring device to monitor your ammonia application? Find more info about the analyzer:
https://www.trace-gas.com/gas-analyzers/las-analyzer/las-nh3/